ding
What is ding?
ding is a client-server thing written in python. Its aim is to execute a set of commands remotely which can be set in the server's config file.
How does it work?
The server awaits commands sent by the client. A command must be defined in the server's config file, else the server won't do anything.
What about ding's security?
The authentication is done by an SSL Client Certificate signed by an (own generated) Certificate Authority. The scripts for generating a CA and signing a Server/Client Certificate are also in here to make it (relatively) easy. [ You need only to press enter in the most cases, type in some certificate information and entering a previously defined CA password. ]
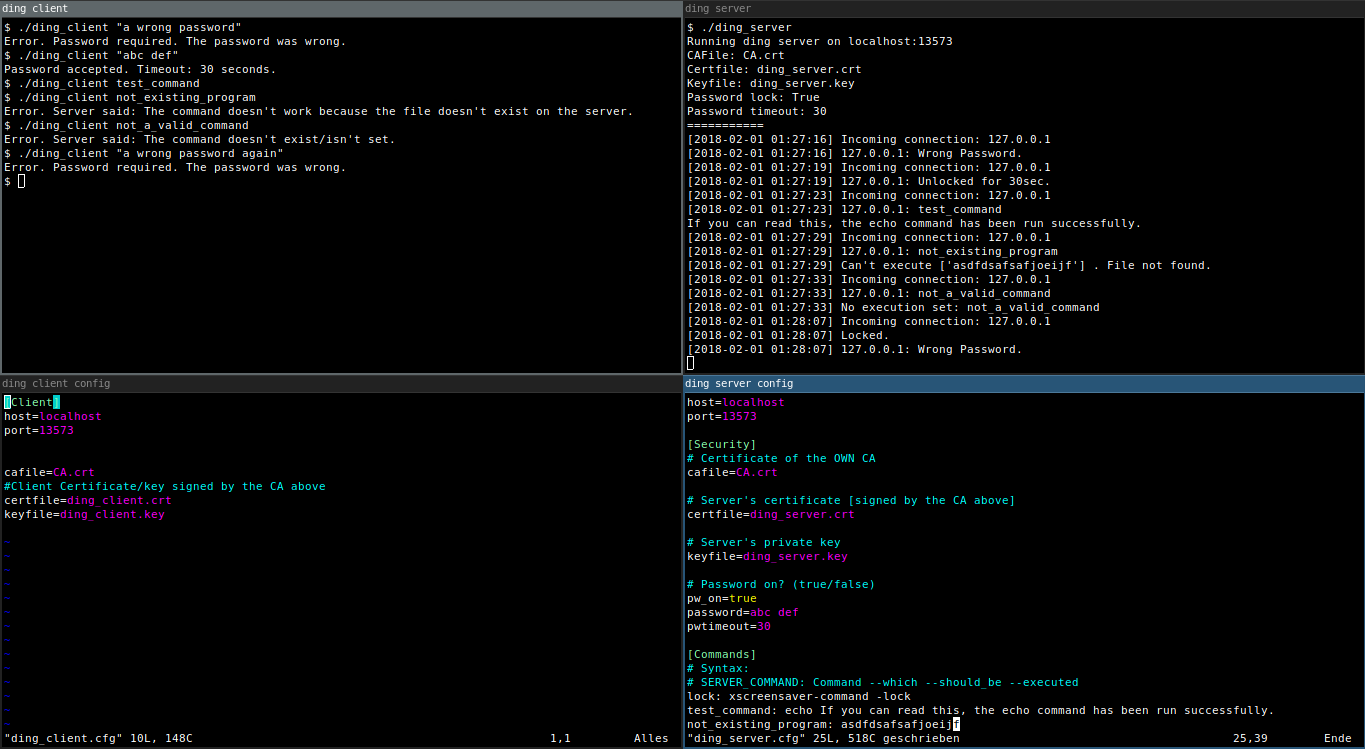
Pic or didn't happen
Installation
In all steps please read carefully what the certification generate scripts want from you. The certificate information needn't to be true at all and can be random. They only need to be different from each other.
- Run
./1_generateCA.shto generate a CA. - Run
./2_generateServCert.shto generate a signed Server Certificate. - Run
./3_generateClientCert.shto generate a signed Client Certificate. - Move
ding_client,ding_client.cfg,ding_client.crt,ding_client.keyandCA.crtto the computer which should be able to send commands to the server. - Do some configuration on the server and client (ding_server.cfg, ding_client.cfg).
- Start the server using
./ding_server. You may want to put this in a tmux session ([Ctrl+B, D] ;) ). - Try out the client using
./ding_client <command>.
Optional: Cleartext password with timeout
If you want to be sure that the ability of the remote connection won't be abused by bad people using your computer, you may want to add a password.
To do so:
- Open your
ding_server.cfg. - Set
pw_on=true. - Set a password, like
password=abc def. - Set a password timeout:
pwtimeout=10for 10 seconds.
If you have a password with special characters like spaces or something else, you might want to embrace the password in quotation marks, like ./ding_client "abc def".